Problema de publicación de rutas en OSPF
Fecha: 22 de mayo del 2018
Escenario
Este escenario propone estudiar un “hueco” que puede quedar en una topología OSPF en donde para
alcanzar una red tenemos varios caminos, y la red destino puede quedar dividida o segmentada debido
a fallas o inconvenientes de capas 1 o 2. Este escenario se me presentó en una situación real y esta es
la maqueta para encontrar la solución adecuada y llevarla a un entorno real de producción.

Los problemas de capa 1 o 2 se podrían solucionar con enlaces redundantes entre switchs, etc, pero
los escenarios reales a veces no lo permiten (falta de pelos de fibra, etc).
Esta maqueta sólo se concentra en buscarle la vuelta al OSPF.
1.- Verificación inicial:
1.1.- Verificación de vecinos OSPF:
Remoto#sh
ip ospf nei
Neighbor ID
Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
192.168.1.2 1
FULL/BDR
00:00:34 10.0.0.3 GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.1.1 1
FULL/DROTHER 00:00:35 10.0.0.2 GigabitEthernet0/1
Remoto#
1.2.- Verificación de la ruta de test:
Remoto#sh
ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R
- RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D -
EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF,
IA - OSPF inter area
N1
- OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
*
- candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P
- periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.0.0.0/29 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L
10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/2] via
10.0.0.3, 00:06:38, GigabitEthernet0/1
[110/2] via 10.0.0.2, 00:06:38, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.2.0/24 is variably
subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Remoto#
2.- Se dispara una falla de conectividad en la red 192.168.1.0/24:
Podrían ser varios motivos, cortes de fibra o cobre, bucles, o cualquier problema que mantenga la capa 1 UP (con link).
Imaginemos que por un tema de spanning-tree, un puerto del Switch2 queda en estado de bloqueo por inconsistencias
en la red (en este caso Switch1 se anunció como root de la topología y Switch2 -el verdadero root- protege la topología
bloqueando el puerto Gi0/1). En este caso, el router Local-A sigue con la interface Gi0/0 de la red LAN 192.168.1.0/24 en
UP-UP y por lo tanto anuncia por OSPF la red 192.168.1.0/24 como válida, aunque sin conectividad local.

2.1.- Verificamos en
Switch2:
Switch2#
%SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARDBLOCK: Port 0/1 tried to
become non-designated in VLAN 1.
Moved to root-inconsistent state
Switch2#
2.2.- Verificamos en router Local-A:
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.1.3 on
GigabitEthernet0/0 from EXSTART to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.1.3 on
GigabitEthernet0/0 from EXSTART to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or
detached
Local-A#sh
standby
GigabitEthernet0/0 - Group 1
State is Active
8
state changes, last state change 00:23:23
Virtual
IP address is 192.168.1.1
Active
virtual MAC address is 0000.0C07.AC01
Local
virtual MAC address is 0000.0C07.AC01 (v1 default)
Hello
time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next
hello sent in 0.581 secs
Preemption disabled
Active
router is local
Standby
router is unknown
Priority 110 (configured 110)
Group name
is hsrp-Gig0/0-1 (default)
Local-A#
2.3.- Verificamos en router Local-B:
Local-B#
%HSRP-6-STATECHANGE: GigabitEthernet0/0 Grp 1
state Standby -> Active
Local-B#sh
standby
GigabitEthernet0/0 - Group 1
State is Active (tampoco hay comunicación HSRP por
lo tanto ambos son active)
10 state changes, last state change 00:41:29
Virtual
IP address is 192.168.1.1
Active
virtual MAC address is 0000.0C07.AC01
Local
virtual MAC address is 0000.0C07.AC01 (v1 default)
Hello
time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next
hello sent in 2.116 secs
Preemption disabled
Active
router is local
Standby
router is unknown
Priority 100 (default 100)
Group
name is hsrp-Gig0/0-1 (default)
Local-B#
2.4.- Verificamos en router Remoto:
Remoto#sh
ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R
- RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D
- EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF,
IA - OSPF inter area
N1
- OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
*
- candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P
- periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.0.0.0/29 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L
10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/2] via
10.0.0.3, 00:22:33, GigabitEthernet0/1 (esta ruta
lleva al segmento de red “útil”)
[110/2] via 10.0.0.2, 00:22:33, GigabitEthernet0/1 (esta ruta lleva al
segmento de red “aislado”)
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Remoto#
3.- Solución al problema de la publicación de la red UP pero “aislada”:
Esta función funciona sólo con la versión 15.4(3), estas pruebas sólo están limitadas a equipos nuevos y con contrato,
por ahora este IOS es figurita difícil.
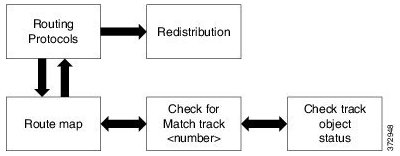
3.1.- Creamos un sensor de conectividad:
Local-A(config)#ip sla 10
Local-A(config-ip-sla)#icmp-echo 192.168.1.10
Local-A(config-ip-sla-echo)#exit
Local-A(config)ip sla schedule 10 start-time now life forever
Local-A(config)#
3.2.- Lo asociamos a un track (tracking de la ruta):
Local-A(config)#track 10 ip sla 10 reachability
Local-A(config-track)#exit
Local-A(config)#
3.3.- Creamos un route-map y lo asociamos al track:
Local-A(config)#route-map OSPF permit 10
Local-A(config-route-map)# match track 10
Local-A(config-route-map)# exit
Local-A(config)#
3.4.- Asociamos el route-map a la redistribución de OSPF:
Con esto la ruta directamente conectada será redistribuída por OSPF.
Local-A(config)#router ospf 1
Local-A(config-router)#no network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Local-A(config-router)#redistribute connected route-map OSPF
% Only classful networks will be redistributed
Local-A(config-router)#end
Local-A#
3.5.- Verificamos:
Local-A#sh
ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 10
Type of operation: icmp-echo
Latest RTT: 1 milliseconds
Latest operation start time: 18:34:05 UTC Mon
May 14 2018
Latest operation return code: OK
Number of successes: 1
Number of failures: 1
Operation time to live: Forever
Local-A#
Local-A#sh
track 10
Track 10
IP SLA
10 reachability
Reachability is Up
2 changes, last change 00:02:57
Latest
operation return code: OK
Latest
RTT (millisecs) 1
Local-A#
3.6.- Verificamos en
router Remoto:
Remoto#sh
ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R
- RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D -
EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF,
IA - OSPF inter area
N1
- OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
*
- candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P
- periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.0.0.0/29 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L
10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O E2 192.168.1.0/24 [110/20] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1
[110/20] via 10.0.0.3, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Remoto#
3.7.- Caída de la red:
Local-A#sh
ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 10
Type of operation: icmp-echo
Latest RTT: NoConnection/Busy/Timeout
Latest operation start time: 16:29:20 UTC Fri
May 18 2018
Latest operation return code: Timeout
Number of successes: 4
Number of failures: 2
Operation time to live: Forever
Local-A#sh
track
Track 10
IP SLA
10 reachability
Reachability is Down
9
changes, last change 00:00:15
Latest
operation return code: Timeout
Tracked
by:
Route-map OSPF
Local-A#
3.8.- Verificación:
Remoto#sh
ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R
- RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D
- EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF,
IA - OSPF inter area
N1
- OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
*
- candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P
- periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.0.0.0/29 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L
10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O E2 192.168.1.0/24 [110/20] via 10.0.0.3, 00:02:13, GigabitEthernet0/1
(esta ruta lleva al segmento de red “útil”)
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Remoto#
4.- Opción 2 (funciona con versiones mas añejas):
4.1.- Creamos un sensor de conectividad:
Local-A(config)#ip sla 10
Local-A(config-ip-sla)#icmp-echo 192.168.1.10
Local-A(config-ip-sla-echo)#exit
Local-A(config)ip sla schedule 10 start-time now life forever
Local-A(config)#
4.2.- Lo asociamos a un track (tracking de la ruta):
Local-A(config)#track 10 ip sla 10 reachability
Local-A(config-track)#exit
Local-A(config)#
4.3.- Creamos un script de eventos cuando el SLA no responde:
Cuando el SLA no responde, el track se establece en DOWN, el script retira el segmento de red de la
configuración del OSPF y por lo tanto no publica mas la ruta.
Debemos asegurarnos de que el SLA apunte a una IP crítica, o crear un conjunto de SLAs y asociarlos
a un objeto mediante funciones AND para no desactivar la red culpa de una sola IP que no responda.
Local-A(config)#event manager applet RED-DOWN
Local-A(config-applet)# event track 10 state down
Local-A(config-applet)# action 1.0 cli command "enable"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 3.0 cli command "router ospf 1"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 4.0 cli command "no network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area
0"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 5.0 cli command "end"
Local-A(config-applet)# exit
4.4.- Creamos un script de eventos cuando el SLA responde:
Cuando el SLA responde, el track se establece en UP, el script agrega el segmento de red de la
configuración del OSPF y por lo tanto publica la ruta de forma válida para los usuarios.
Local-A(config-applet)#event manager applet RED-UP
Local-A(config-applet)# event track 10 state up
Local-A(config-applet)# action 1.0 cli command "enable"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 3.0 cli command "router ospf 1"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 4.0 cli command "network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0"
Local-A(config-applet)# action 5.0 cli command "end"
Local-A(config-applet)# end
Local-A#
4.5.- Verificamos:
May 20 23:24:23.031: %TRACKING-5-STATE: 10 ip
sla 10 reachability Down->Up
May 20 23:24:23.079: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I:
Configured from console by on vty0 (EEM:RED-UP)
4.6.- Simulamos corte
de vínculo:
May 20 23:29:28.595: %TRACKING-5-STATE: 10 ip
sla 10 reachability Up->Down
May 20 23:29:28.671: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I:
Configured from console by on vty0 (EEM:RED-DOWN)
Local-A#
4.7.- Verificamos en router Local-A:
Local-A#sh
runn | beg ospf 1
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute connected
network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 (ahora sólo esta red está configurada)
!
---resumido---
Local-A#
Local-A#sh
ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 10
Type of operation: icmp-echo
Latest RTT: NoConnection/Busy/Timeout
Latest operation start time: 23:29:20 UTC Sun
May 20 2018
Latest operation return code: Timeout
Number of successes: 4
Number of failures: 2
Operation time to live: Forever
Local-A#sh
track
Track 10
IP SLA
10 reachability
Reachability is Down
9
changes, last change 00:00:26
Latest
operation return code: Timeout
Tracked
by:
EEM
applet RED-UP
EEM
applet RED-DOWN
Local-A#
4.8.- Verificamos en
router Remoto:
Remoto#sh
ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R
- RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D
- EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF,
IA - OSPF inter area
N1
- OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
*
- candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P
- periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.0.0.0/29 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L
10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O E2 192.168.1.0/24 [110/20] via 10.0.0.3, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1
(sólo Local-B pubica la ruta)
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Remoto#
4.9.- Reestablecemos
la conectividad:
May 20 23:35:24.071: Track: 10 Change #10 ip
sla 10, reachability Down->Up
May 20 23:35:24.071: %TRACKING-5-STATE: 10 ip
sla 10 reachability Down->Up
May 20 23:35:24.119: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I:
Configured from console by on vty0 (EEM:RED-UP)
4.10.- Verificamos en router Local-A:
Local-A#sh
runn | beg ospf 1
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute connected
network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 (seagregó en la configuración)
!
---resumido---
Local-A#
4.11.- Verificamos en router Remoto:
Remoto#sh
ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R
- RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D
- EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF,
IA - OSPF inter area
N1
- OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
*
- candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P
- periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.0.0.0/29 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L
10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/2] via
10.0.0.3, 00:06:38, GigabitEthernet0/1
[110/2] via 10.0.0.2, 00:06:38, GigabitEthernet0/1 (ahora la ruta está publicada)
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C
192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L
192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Remoto#
5.- Configuración final (Local-A):
Local-A#sh runn (sólo lo relevante)
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2244 bytes
!
!
version 15.4
!
hostname Local-A
!
track 10 ip sla 10 reachability
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip
address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip
address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.248
!
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network
10.0.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip sla 10
icmp-echo 192.168.1.10
ip sla schedule 10 life forever start-time now
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
event manager applet RED-DOWN
event
track 10 state down
action
1.0 cli command "enable"
action
2.0 cli command "conf t"
action
3.0 cli command "router ospf 1"
action
4.0 cli command "no network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0"
action
5.0 cli command "end"
event manager applet RED-UP
event
track 10 state up
action
1.0 cli command "enable"
action
2.0 cli command "conf t"
action
3.0 cli command "router ospf 1"
action
4.0 cli command "network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0"
action
5.0 cli command "end"
!
end
Local-A#
(2018) Networking for lonely nights
Rosario,
Argentina